Color is crucial for elegant data visualization. In our previous article we describe the list of color palettes available in R.
In this current article we define the basics for using the power of color and, we describe an R package and an online tool for generating beautiful color schemes.
Understanding color wheel
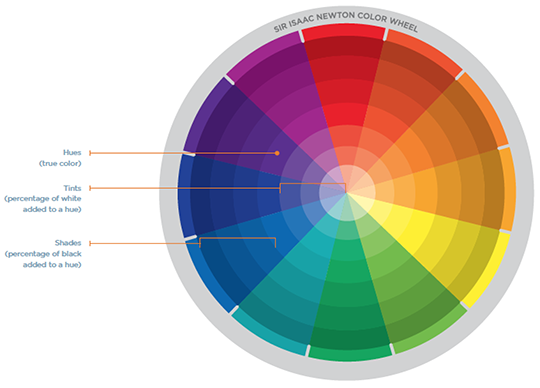
(Image from Nancy Duarte, slide:ology)
The color wheel helps you visualize the relationships between colors.
The wheel is divided into pie slices which have the following components:
- hue (true color): On the wheel above, the hue is four rings out of the center.
- tints: correspond to the colors toward the center of the wheel (= hue + white color)
- shades: corresponds to the ring of colors on the outside of the hue ( = hue + black color)
Defining the basics for choosing colors
Monochromatic: Variations of the same color.
Analogous: colors that are touching in the wheel creates narrow harmonious color scheme.
Complementary: Colors from the opposite ends of the wheel provide the most contrast.
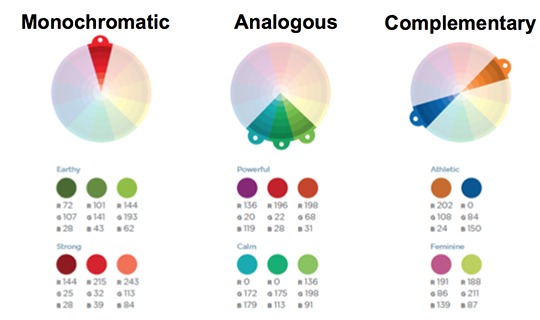
(Image from Nancy Duarte, slide:ology)
Split Complementary: A variation of the complementary scheme that uses two colors on either side of a directly complementary color. These colors have high visual contrast but with less visual tension than purely complementary colors.
Triadic: Three colors equally spaced around the color wheel create vivid visual interest.
Tetradic: Two pairs of complementary colors. This scheme is popular because it offers strong visual contrast while retaining harmony.
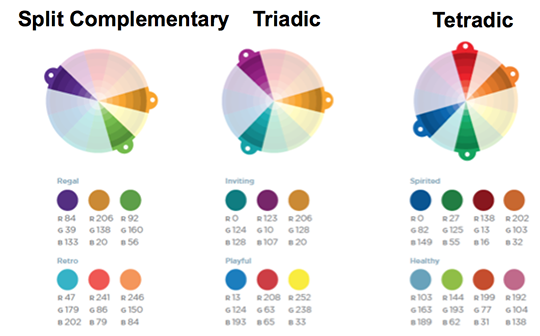
(Image from Nancy Duarte, slide:ology)
colortools: R package for creating easily color schemes in R
The excellent R package colortools developed by Gaston Sanchez is an easy to use solution for generating color schemes in R.
Install colortools
install.packages("colortools")Load colortools
library(colortools)Color wheel
The function wheel() can be used to generate a color wheel for a given color:
wheel("darkblue", num = 12)## [1] "#00008B" "#46008B" "#8B008B" "#8B0046" "#8B0000" "#8B4500" "#8B8B00"
## [8] "#468B00" "#008B00" "#008B45" "#008B8B" "#00468B"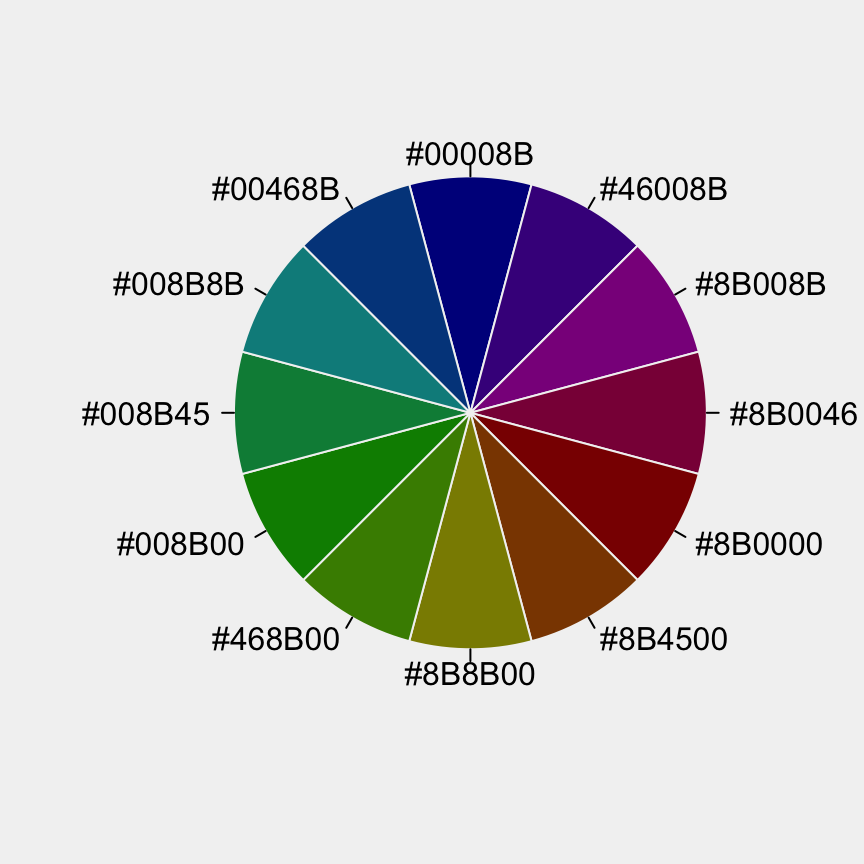
Analogous color scheme
The function adjacent() or analogous() can be used:
analogous("darkblue")## [1] "#00008B" "#46008B" "#00468B"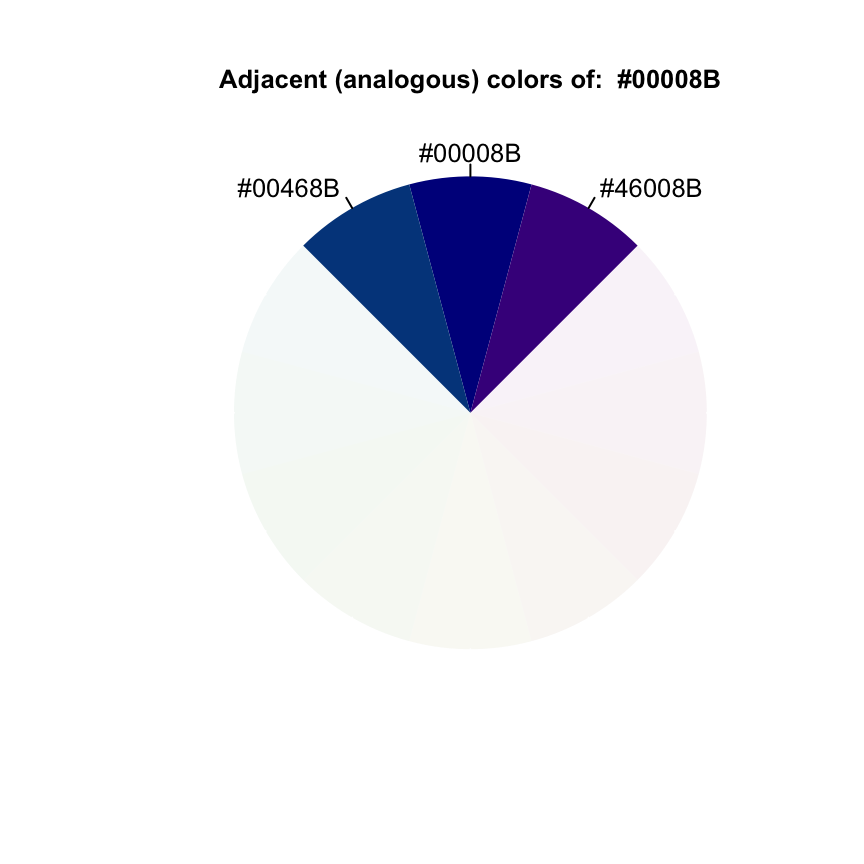
Complementary color scheme
complementary("steelblue")## [1] "#4682B4" "#B47846"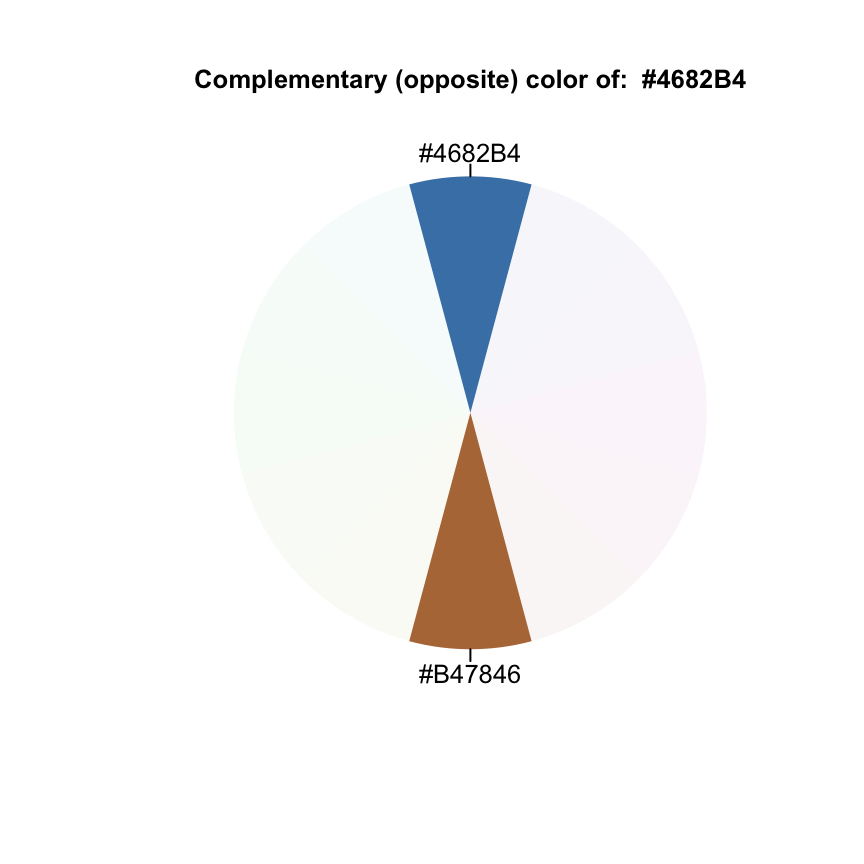
Split Complementary Color Scheme
splitComp("steelblue")## [1] "#4682B4" "#B4464B" "#B4AF46"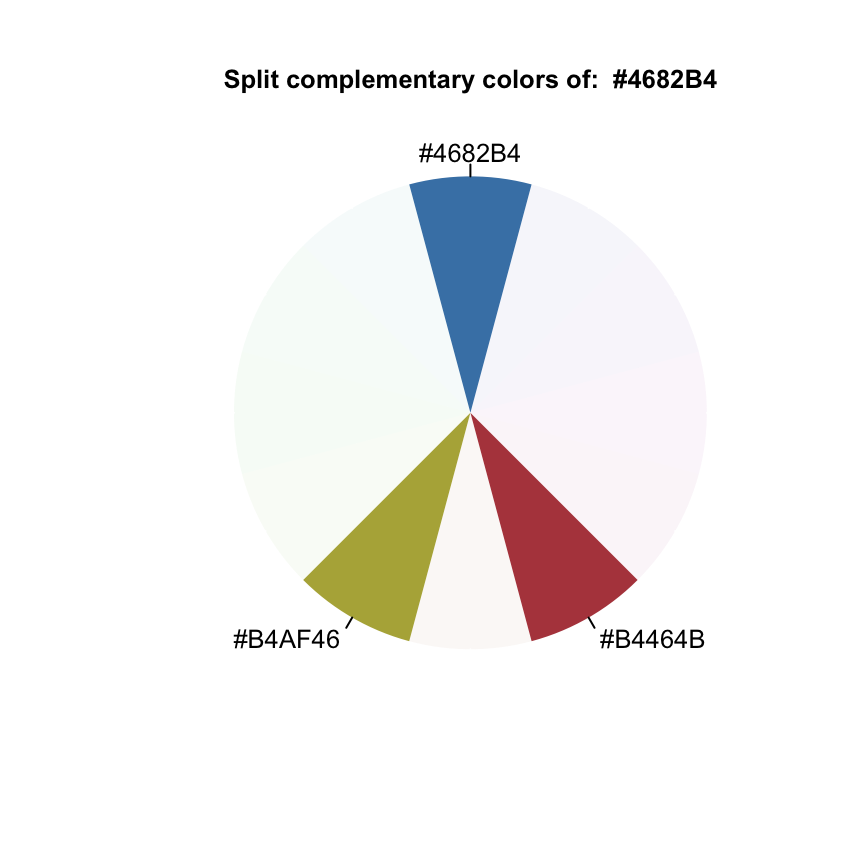
Tetradic Color Scheme
tetradic("steelblue")## [1] "#4682B4" "#7846B4" "#B47846" "#82B446"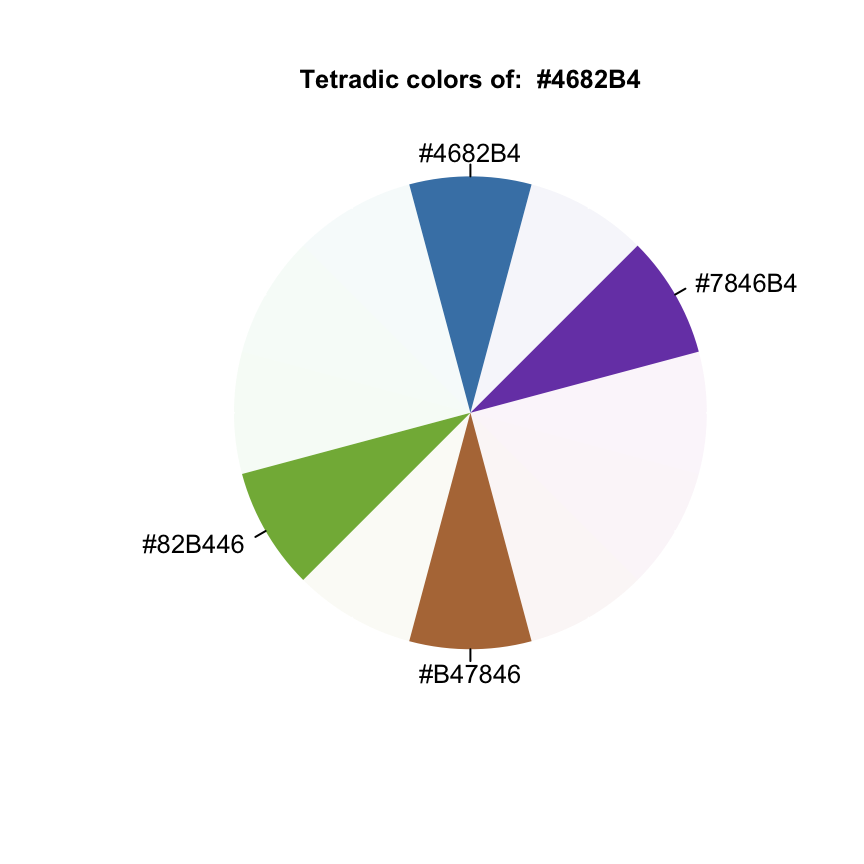
Square color scheme
square("steelblue")## [1] "#4682B4" "#AF46B4" "#B47846" "#4BB446"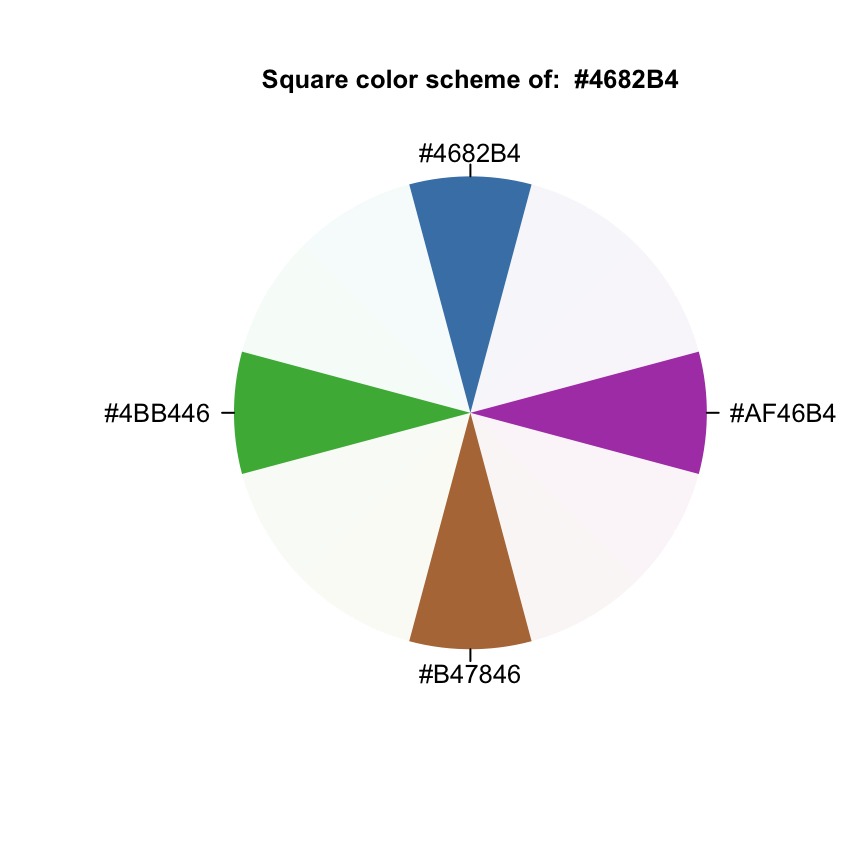
Sequential colors
sequential("steelblue")## [1] "#B4B4B4FF" "#ABB0B4FF" "#A2ACB4FF" "#99A8B4FF" "#90A4B4FF"
## [6] "#87A0B4FF" "#7E9BB4FF" "#7597B4FF" "#6C93B4FF" "#638FB4FF"
## [11] "#5A8BB4FF" "#5187B4FF" "#4883B4FF" "#3F7FB4FF" "#367BB4FF"
## [16] "#2D77B4FF" "#2473B4FF" "#1B6EB4FF" "#126AB4FF" "#0966B4FF"
## [21] "#0062B4FF"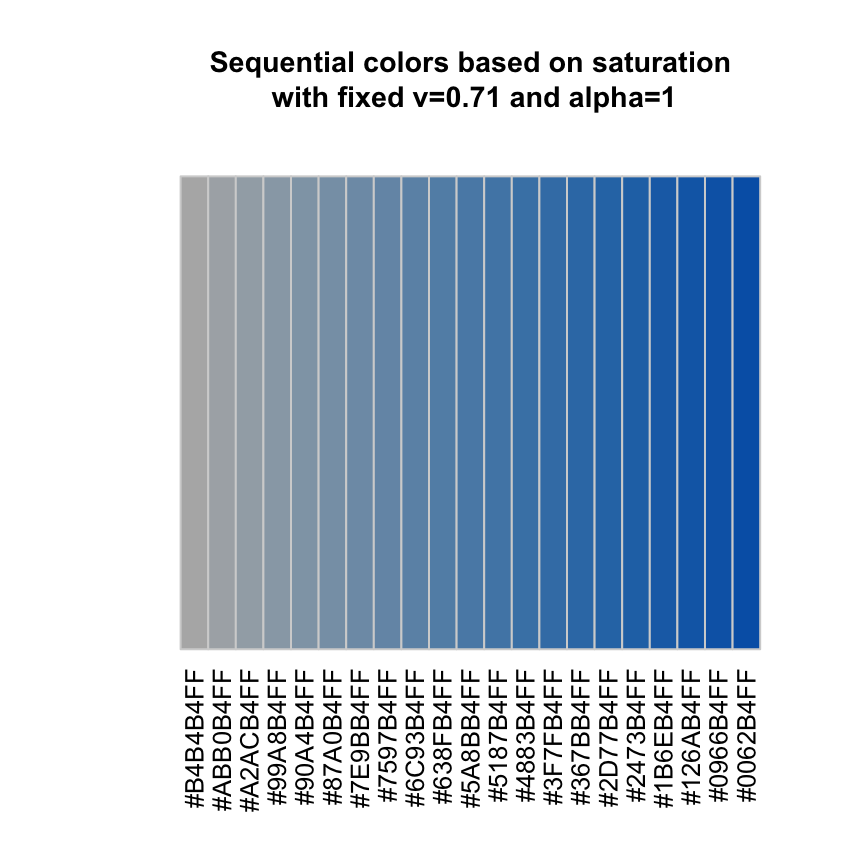
Read more
- slide:ology: The Art and Science of Creating Great Presentations (by Nancy Duarte)
- R package colortools by Gaston Sanchez.
Infos
This analysis has been performed using R software (ver. 3.2.3) and colortools (ver. 0.1.5)